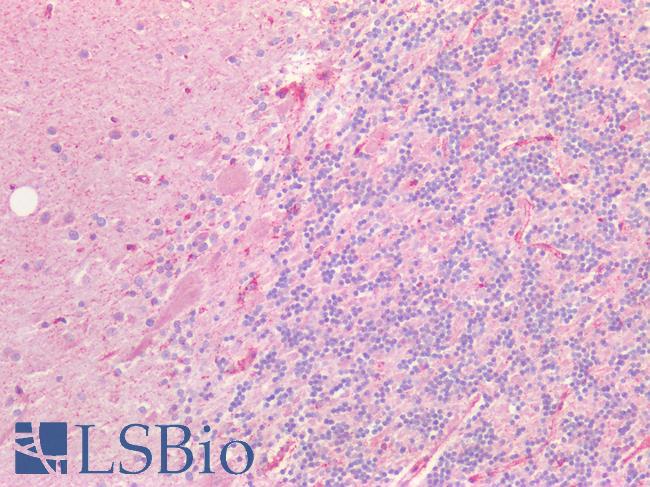
EPH receptor A4 (ephrin type-A receptor 4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHA4 gene.
This gene belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. EPH and EPH-related receptors have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Receptors in the EPH subfamily typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands.
In 2012, a publication in Nature Medicine revealed a connection between EPHA4 and the neurodegenerative disease Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), where a defective gene allows ALS patients to live considerably longer than patients with an intact gene. This opens up for development of treatment for this currently untreatable disease.
References
Further reading
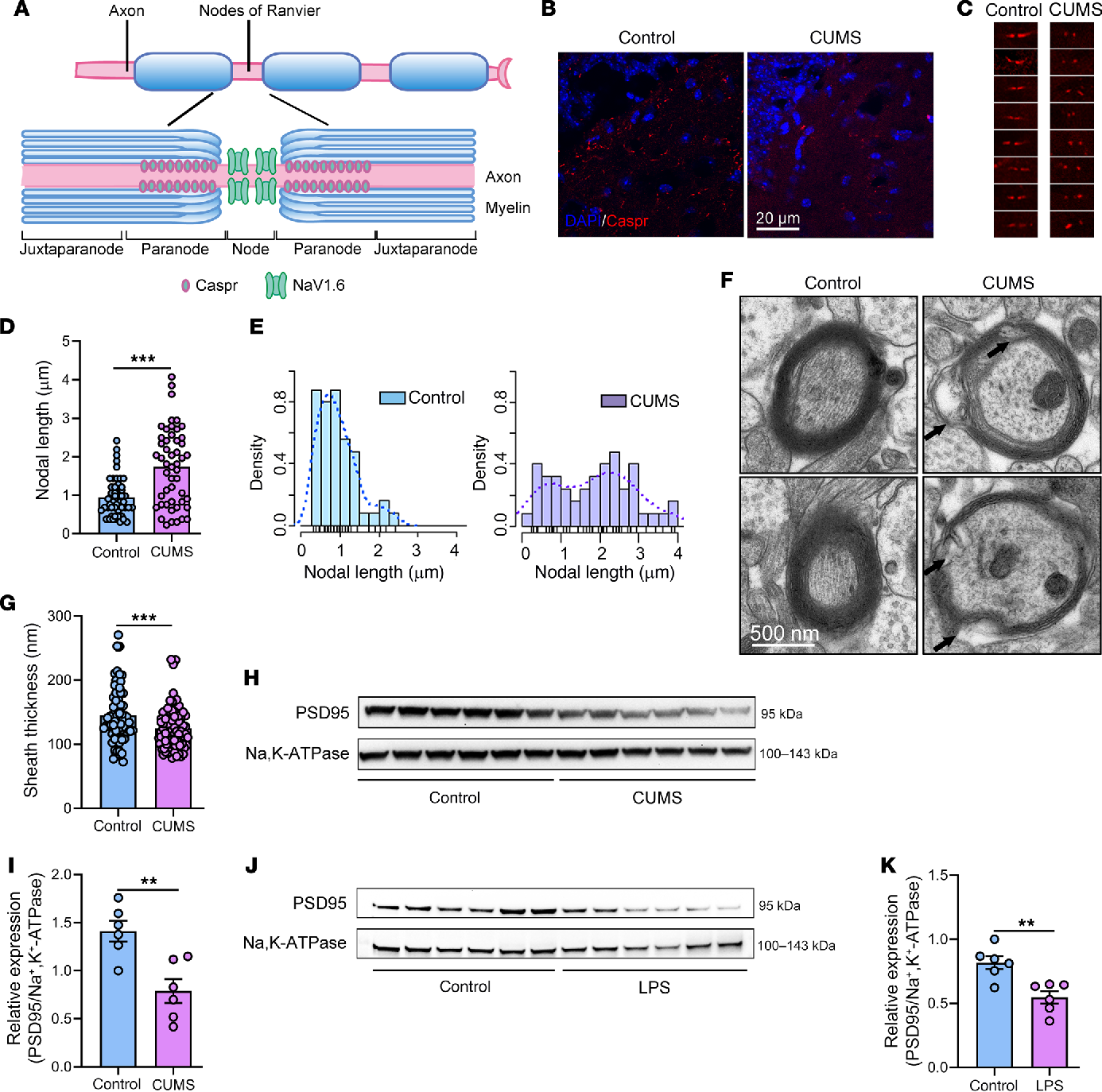
.jpg)